What is Tokenization?
Tokenization is a powerful technique that transforms physical or digital assets into secure digital representations that can be held, sold, and traded on a blockchain. In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the need to protect sensitive data has become paramount. This is where tokenization comes into play – by converting assets into digital tokens, it safeguards data and ensures privacy, making it an essential tool in the digital world.
The Tokenization Process
-
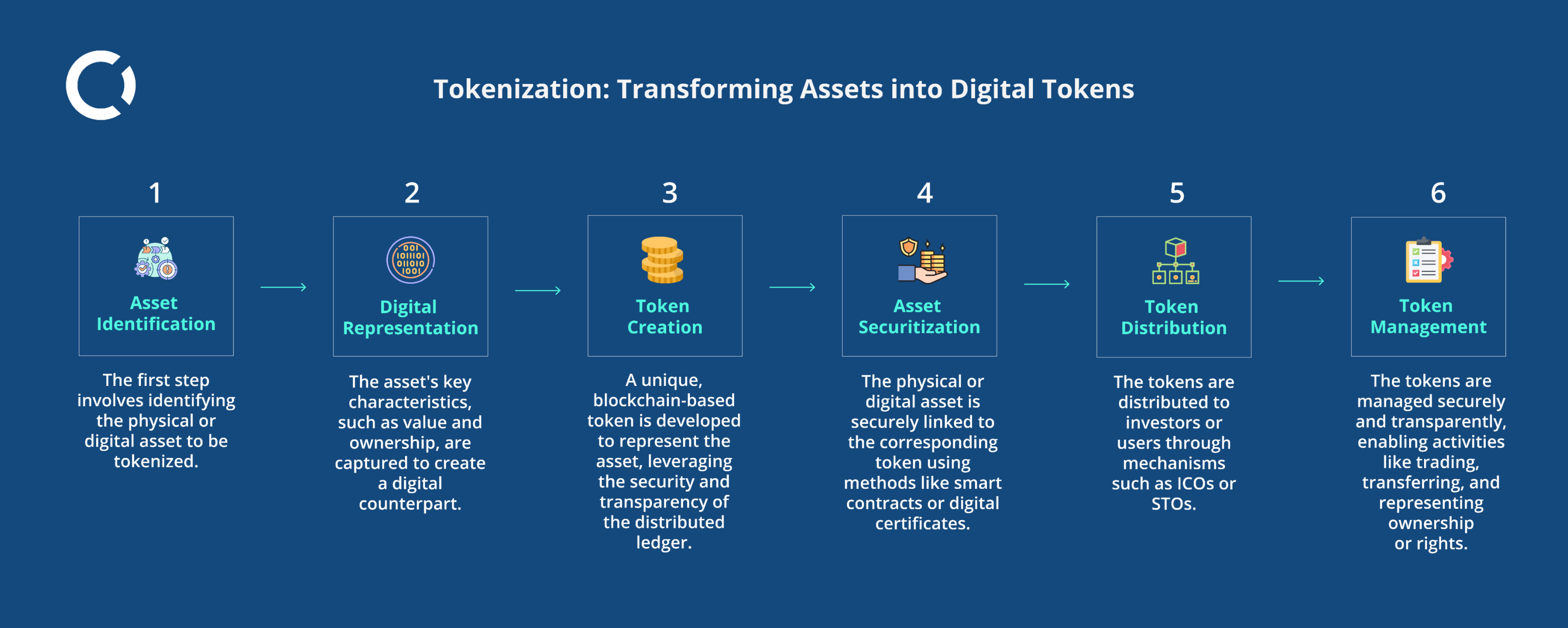
1. Asset Identification
The first step in the tokenization process is to identify the physical or digital asset that requires protection. This could be payment card information, personal identifiers such as social security numbers, or any other sensitive data that needs to be secured.
-
2. Digital Representation
After identifying the asset, the next step is to capture its essential characteristics, such as its value and ownership, and create a digital counterpart. This digital representation serves as the foundation for the tokenization process. It involves mapping the key attributes of the asset into a digital form that can be processed and managed within the tokenization system. Ensuring accuracy and completeness in this step is critical, as it directly impacts the integrity and utility of the resulting token.
-
3. Token Creation
The next stage involves developing a unique, blockchain-based token to represent the asset. This process begins by selecting an appropriate blockchain platform that offers the necessary security features and scalability. By leveraging the inherent security and transparency of the distributed ledger, the token becomes a secure and tamper-resistant digital proxy for the original sensitive data. Each token is cryptographically linked to the underlying asset, ensuring that any attempt to alter the token would be immediately detectable. This cryptographic linkage not only protects the token from tampering but also provides a transparent and verifiable record of ownership and transaction history. The creation of these tokens can involve smart contracts, which automate and enforce the terms of the agreement related to the asset, further enhancing security and efficiency.
-
4. Asset Securitization
To ensure the link between the physical or digital asset and its corresponding token is secure, various methods are employed. One common method is the use of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts automate and enforce the rules and conditions under which the token represents the asset, ensuring that the token accurately reflects the asset’s value and ownership. Another method is the use of digital certificates, which serve as electronic documents that verify the authenticity and ownership of the asset. These certificates can be stored on the blockchain alongside the token, providing an additional layer of security and verification. This process of asset securitization creates a robust and verifiable connection between the original asset and its digital representation. It ensures that any changes or transfers of ownership are transparent and traceable, making the tokenization process both secure and reliable.
-
5. Token Generation
A key step in the tokenization process is generating the unique token. This involves using specialized algorithms or services designed for tokenization. These algorithms take the original sensitive data and transform it into a secure and unique token. Techniques used include:
- Encryption: Converts the data into a coded form that can only be read if decrypted with the correct key, ensuring that the tokenized data cannot be easily accessed or understood by unauthorized parties.
- Hashing: Creates a fixed-size string of characters from the original data using a mathematical function. This process is one-way, meaning the original data cannot be easily retrieved from the hash, adding an extra layer of security.
- Format-preserving transformation: Alters the data while maintaining its original format, which is particularly useful when the token needs to fit into a specific data structure or format without changing how the data looks. These techniques collectively help generate tokens that are not only secure but also retain the necessary characteristics to be useful in the system or application where they will be used. This ensures that the tokenized data maintains its integrity and can be safely utilized without compromising security.
-
6. Token Storage and Retrieval
After the tokens are generated, they need to be securely stored in a centralized token vault or repository. This repository acts as a secure storage location where all tokens are kept safe. To protect the tokens from unauthorized access or data breaches, strong access controls and security measures are put in place. These controls include strict authentication procedures, encryption of stored tokens, and regular security audits to detect and address any vulnerabilities. In addition to storage, it’s crucial to have efficient processes for retrieving the original sensitive data from the tokens when needed. This retrieval process ensures that only authorized parties can access the original data, maintaining the security and privacy of the sensitive information. By implementing these secure storage and retrieval methods, organizations can ensure that their tokenized data remains protected and accessible only to those with the necessary permissions, thereby safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of the data.
-
7. Token Replacement
In the final step, the original sensitive data is replaced with the generated tokens within the application or system. This ensures that tokens can be used just like the original data, maintaining the system’s normal operations without any disruptions. Additionally, processes are put in place to update or replace tokens when necessary, such as when the original data needs to be updated or when a token is compromised.
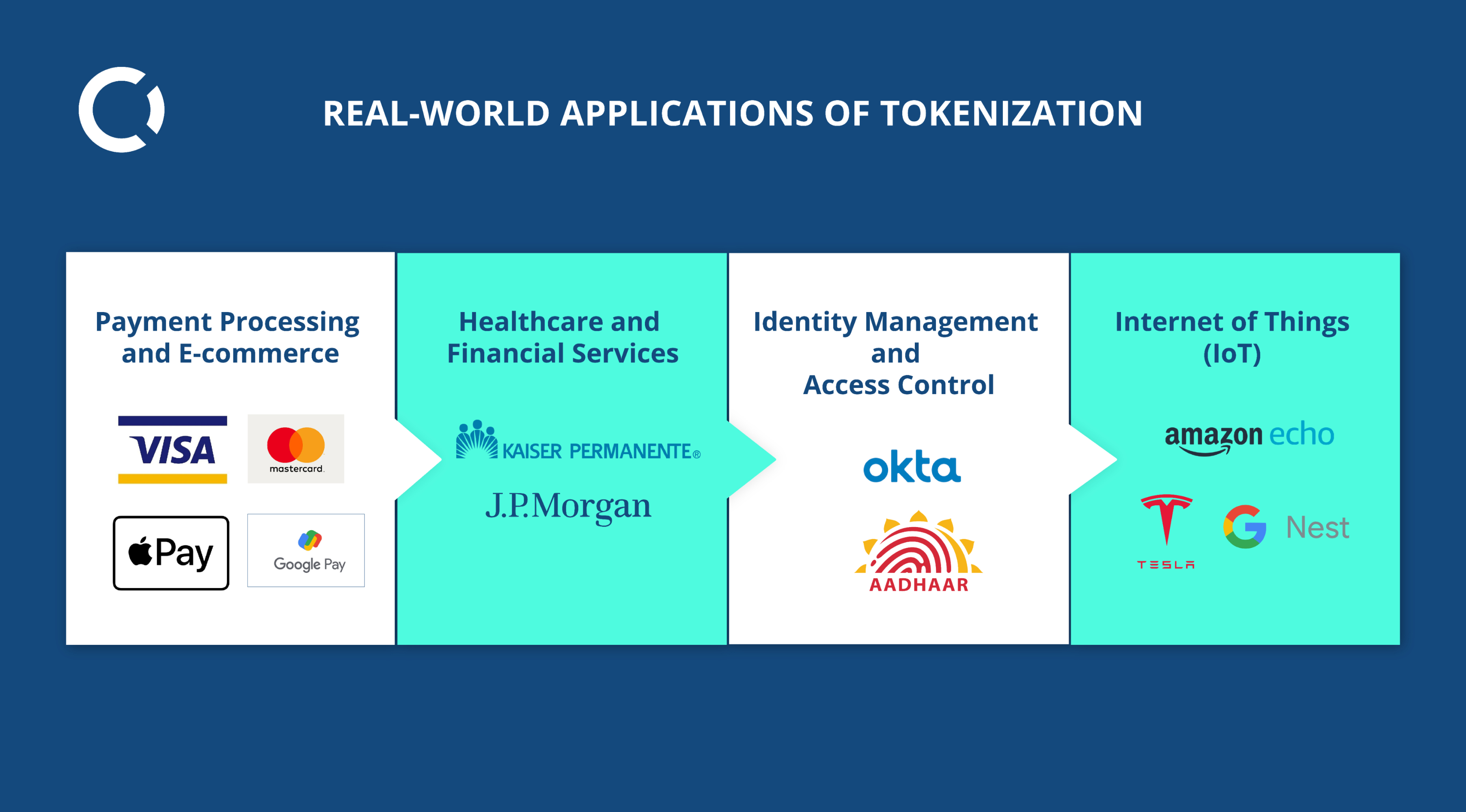
Real-world Applications of Tokenization
Tokenization has found widespread adoption across various industries and use cases, demonstrating its versatility and importance in the digital landscape.
-
Payment Processing and E-commerce:Example:
- Visa and Mastercard use tokenization to secure payment card information. When you make an online purchase, the actual card number is replaced with a token. This ensures that even if the data is intercepted, the actual card number is not exposed, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Apple Pay and Google Pay use tokenization to enable secure, contactless payments. Instead of transmitting card details, a unique token is used for each transaction, enhancing security.
-
Healthcare and Financial Services:Example:
-
- The healthcare provider, Kaiser Permanente, uses tokenization to protect patient records. By tokenizing personal health information (PHI), they ensure that sensitive data is secure during storage and transmission, complying with regulations like HIPAA.
- Financial institutions like JPMorgan Chase use tokenization to safeguard customer data, including account numbers and personal identifiers. This helps in preventing identity theft and ensuring secure transactions.
-
Identity Management and Access Control:Example:
-
- Okta, an identity management service, uses tokenization to securely represent and authenticate user identities. This ensures that sensitive authentication details are protected, enhancing security for enterprise clients.
- Government ID programs, such as Aadhaar in India, tokenize personal identifiers to enhance the security of citizen data during authentication processes.
-
Internet of Things (IoT):Example:
-
- Smart home devices like Amazon Echo and Google Nest use tokenization to secure communication between devices and servers. This prevents unauthorized access and ensures that sensitive data, such as voice commands and personal preferences, remain protected.
- In the automotive industry, companies like Tesla use tokenization to secure data transmission between connected cars and their servers, ensuring the privacy and security of vehicle and driver information.
Conclusion
Tokenization is a transformative technology that has become a cornerstone of data security and privacy in the digital world. By converting sensitive data into secure digital representations, tokenization empowers organizations to protect their assets, comply with regulations, and build trust with their customers. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the importance of tokenization will only grow, making it a crucial consideration for businesses and individuals alike. By understanding the intricacies of the tokenization process and its real-world applications, we can unlock the full potential of this technology and ensure the safety and privacy of our digital assets.
Embrace Decentralization with Codora
Curious about how blockchain solutions can enhance your data security? Contact Codora today at hello@codora.io and discover how we can help safeguard your assets and ensure your privacy in the digital age!